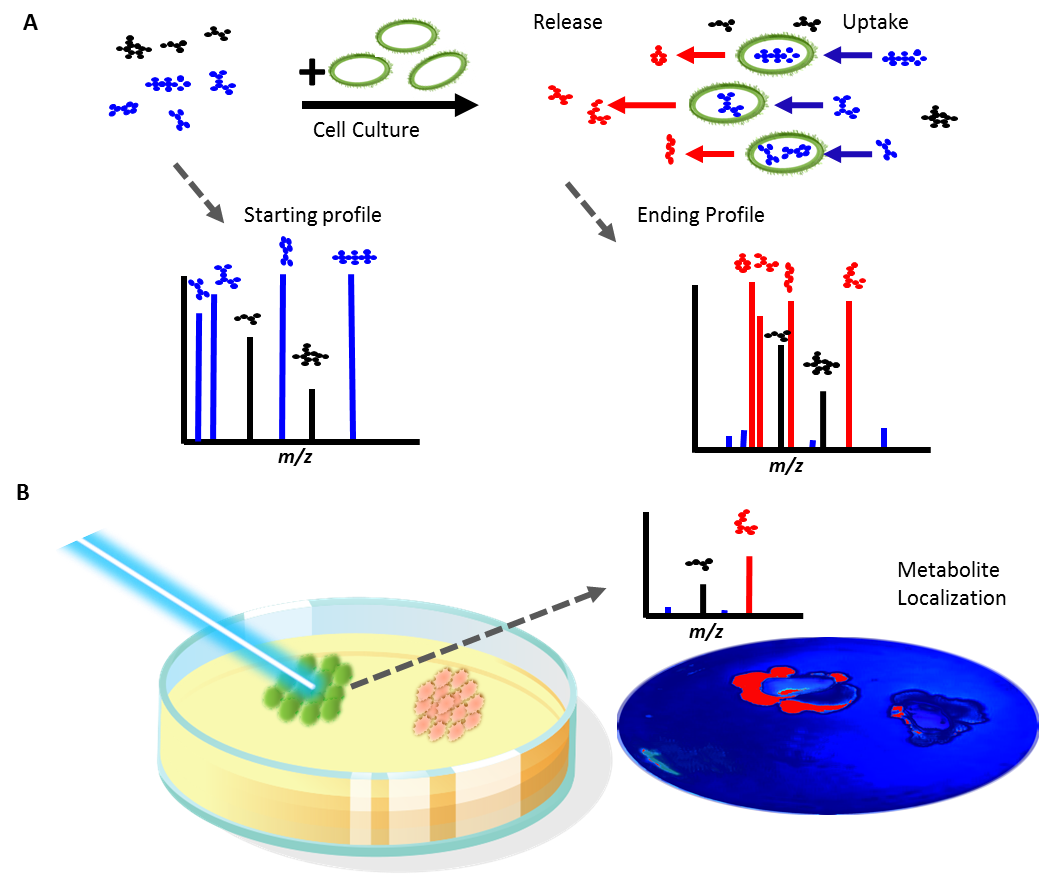
We have a new publication with scientists at the University of California Davis and the University of Texas at Austin: “Bioactive Diterpenoids Impact the Composition of the Root-Associated Microbiome in Maize (Zea mays).” Metabolomics analysis identified dolabralexin diterpenoids as metabolites that influence the rhizosphere and bacterial communities associated with maize. As a major crop, maize is often studied to determine methods of improving crop yield and increasing stress resilience. This research is an exciting step toward understanding the role of metabolites in plant-microbe interactions.
The paper is the result of the metabolomics program at the DOE JGI Community Science Program. For more information visit the JGI Metabolomics Program website.
Read the recent publication here.